7 QC Tools you should use to improve your Garments/Sweater product
quality:
7 QC (Quality Control) tools
are very effective for Garments/Sweater or any other types of the factory to
solve almost every type of problem in a factory operation. These are the tools
of troubleshooting quality issues, based on numeric value. 7 QC tools in Garments/Sweater
industry is a set of data analysis tools used to support continuous quality
improvement efforts. If you can use these seven fundamental tools, then
definitely quality control will be effective for your company.
7 QC Tools in Garments/Sweater
Industry:
Histogram
Check Sheet (Daily Inspection
Finding Report)
Cause-and-Effect Diagram
Pareto Chart
Scatter Diagram
Control Chart
Stratification
7 QC Tools in Garments/Sweater
Industry
Benefits of 7 QC Tools:
Improve management decision
making skills
Collect, present, Identify and
analyses data
Implement Six Sigma
Control cost of poor quality
Reduce variations and improve
quality
Reduce defects and improve
production
Reduce cycle time and improve
efficiency
Continuous quality improvement
Encourages teamwork and
confidence
Enhances customer satisfaction
through improved quality product
Explanation of 7 QC Tools for Garments/Sweater
Industry
Histogram:
Histogram is also a bar chart.
It is a graphical chart based on numeric value for showing frequency
distribution of database. People become confused among Histograms and Bar
Charts. A histogram is used for continuous data, where the bins represent
ranges of data, while a bar chart is a plot of categorical variables. Some
authors recommend that bar charts have gaps between the rectangles to clarify
the distinction.
Check Sheet (Daily Inspection Finding Report):
The Check Sheet/Tally sheet is
a simple document that is used for collecting data in real time and at the
location where the data is generated. The document is typically a blank form
that is designed for the quick, easy, and efficient recording of the desired
information, which can be either quantitative or qualitative. When the
information is quantitative, the check sheet is sometimes called a tally sheet.
A tally sheet to collect data on frequency of occurrences which custom designed
by user.
Cause-and-effect diagram
(Ishikawa Diagram / Fishbone Diagram):
Cause-and-effect diagram is
look like a fish that’s why it’s called Fishbone Diagram, also called Ishikawa
diagram, herringbone diagrams or Fishikawa diagrams, a visualization tool for
categorizing the potential causes of a problem in order to identify its root
causes. Causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa that show the causes of a
specific event. Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa developed the “Fishbone Diagram” at the
University of Tokyo in 1943.To break down (in successive layers of detail) root
causes that potentially contribute to a particular effect. This diagram is used
in process improvement methods to identify all of the contributing root causes
likely to be causing a problem.
How to Work on Fishbone
If you find a problem and want
to make fishbone diagram. First need brainstorming about the defect to find out
types of causes based on 6 basic things. These are:
Machine
Manpower
Environment
Method
Materials
Measurement
Brainstorm all the possible
causes of the problem. Ask: “Why does this happen?” As each idea is given, the
facilitator writes it as a branch from the appropriate category. Causes can be
written in several places if they relate to several categories. For example you
can see fishbone in the below:
Pareto Chart (80/20 Rule):
A Pareto chart is a bar graph.
The lengths of the bars represent frequency or cost (time or money), and are
arranged with longest bars on the left and the shortest to the right. In this
way the chart visually depicts which situations are more significant.
The Pareto principle
The Pareto principle (also
known as the 80–20 rule, the law of the vital few, and the principle of factor
sparsity) states that, for many events, roughly 80% of the effects come from
20% of the causes. More generally, the Pareto Principle is the observation (not
law) that most things in life are not distributed evenly. In Garments/Sweater
industry, you can see the data in the below that first 5 defects covered 50% of
total defect. So 80-20 rules will not cover all-time 80% problem for 20% causes.
It can mean all of the following things:
20% of the defects number
accumulate 80% of the total defects
20% of the operator produce 80%
of the defects
20% of the customers create 80%
of the revenue
Pareto for Garments/Sweater
Industry
Scatter Diagram:
The scatter diagram graphs
pairs of numerical data, with one variable on each axis, to look for a
relationship between them. If the variables are correlated, the points will
fall along a line or curve. The better the correlation, the tighter the points
will hug the line. The scatter diagram Collect pairs of data where a
relationship is suspected.
Control Chart (Shewhart
Chart):
Control charts, also known as
Shewhart charts or process-behavior charts, are a statistical process control
tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of
control. A control chart shows how data frequency changes, defects trends and
compares with previous time record. Control chart monitor process and
hypothetical prediction. Garments/Sweater industry need to reduce defect
frequency to get quality improvement.
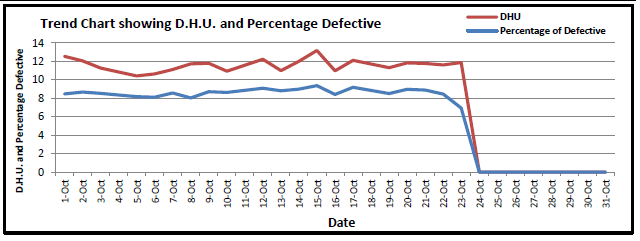
Control Chart for Garments/Sweater:
Stratification (Divide and
Conquer), can be alternative of flow chart or run chart
Stratification is a method of
dividing data into subcategories and classify data based on a group, division,
class or levels that helps in deriving meaningful information to understand an
existing problem. The main purpose of Stratification is to divide the data and
conquer the meaningful information to solve a problem. The visual nature of the
chart makes patterns jump out.
Implementation of 7 QC Tools
To implement these tools in
your industry, you must have to do Pareto, Fishbone for every section. Result
publishes visibly in each line or area in board. People will be conscious to
reduce defect. There improvement tracking on control chart also visible for
each line/area. You have to find root cause from the root level for cause and
effect diagram. Data and data collection must be accurate. Every section has to
be taken corrective action based on quality data. Every section must do a
quality meeting to take new decision for quality control at least once per
month.

















1 Comments
Good tools, can you support us with this tools. Iitgarmentsindia.
ReplyDelete